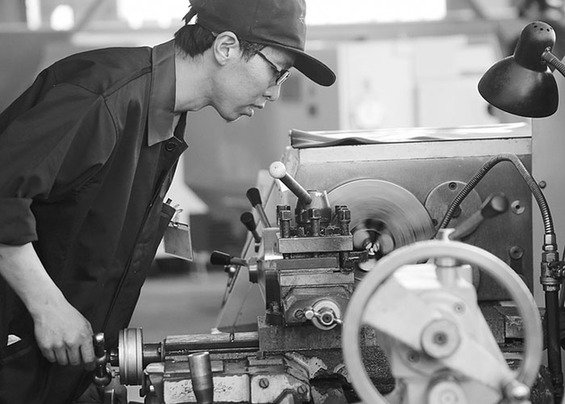
Introduction
Precision is a fundamental aspect of the machining industry. The ability to produce parts with exact specifications and tight tolerances is critical in ensuring the performance and reliability of a wide range of products, from aerospace components to medical devices. This article explores the importance of precision in machining and the methods used to achieve it.

Why Precision Matters
Precision in machining is crucial for several reasons:
Interchangeability: Parts that fit together perfectly can be easily replaced or assembled, which is essential in mass production and maintenance.
Performance: High-precision parts contribute to the optimal performance of machines and devices. For example, in the automotive industry, precise engine components ensure better fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
Safety: In industries like aerospace and healthcare, the safety of products depends on the accuracy of machined parts. A minor deviation in a component can lead to catastrophic failures.
Cost Efficiency: Precision reduces the need for additional finishing processes and rework, saving time and money.
Achieving Precision in Machining
To achieve the required precision, the machining industry employs several techniques and technologies:
Advanced CNC Machines: Modern CNC machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances. These machines are capable of making precise movements based on programmed instructions, minimizing human error.
High-Quality Cutting Tools: The selection of cutting tools is critical. Tools made from high-quality materials, such as carbide and diamond, maintain their sharpness and dimensional accuracy over longer periods.
Stable Machining Conditions: Factors such as temperature, vibration, and tool wear can affect precision. Maintaining stable machining conditions through proper cooling, lubrication, and machine calibration is essential.
Inspection and Measurement: Accurate measurement tools and inspection techniques, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), ensure that parts meet the specified tolerances. Regular inspection helps identify and correct deviations early in the process.
Challenges in Precision Machining

While precision machining offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges:
Complex Geometries: Producing parts with complex shapes and features can be difficult and requires advanced machines and skilled operators.
Material Variability: Different materials react differently to machining processes. Understanding the properties of each material is crucial to achieving precision.
Cost: High-precision machining often requires significant investment in equipment, tools, and training. Balancing precision with cost-effectiveness is a common challenge.
Conclusion
Precision is the backbone of the machining industry, enabling the production of high-quality, reliable parts that are essential in many sectors. By continually improving machining technologies and techniques, the industry can meet the increasing demands for precision and maintain its critical role in manufacturing.