Introduction
Automation has become a key driver of efficiency and innovation in the machining industry. By incorporating automated systems, manufacturers can increase productivity, improve quality, and reduce costs. This article examines the role of automation in modern machining and its impact on the industry.

The Benefits of Automation
Increased Productivity: Automated machines can operate continuously, without the need for breaks. This leads to higher output and faster production cycles.
Improved Quality: Automation reduces the risk of human error, ensuring consistent quality and precision. Automated systems can perform complex tasks with high accuracy.
Cost Reduction: While the initial investment in automation can be high, the long-term savings from increased efficiency, reduced waste, and lower labor costs are substantial.
Enhanced Safety: Automation reduces the need for human operators to perform dangerous tasks, improving workplace safety and reducing the risk of accidents.
Types of Automation in Machining
Robotic Automation: Industrial robots are used for tasks such as loading and unloading parts, assembly, and inspection. Robots can handle repetitive tasks with high precision and speed.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs transport materials and parts within a manufacturing facility, improving logistics and reducing manual handling.
CNC Automation: CNC machines with advanced automation features, such as tool changers and part feeders, can operate with minimal human intervention.
Software Automation: Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software automates the programming of CNC machines, optimizing tool paths and machining processes.
Challenges of Implementing Automation
High Initial Costs: The upfront cost of purchasing and integrating automated systems can be significant. Companies need to evaluate the long-term benefits to justify the investment.
Skilled Workforce: Automation requires a skilled workforce to program, operate, and maintain the systems. Training and upskilling employees is essential.
Integration Complexity: Integrating automation into existing processes can be complex. Careful planning and execution are needed to ensure a smooth transition.
The Future of Automation in Machining
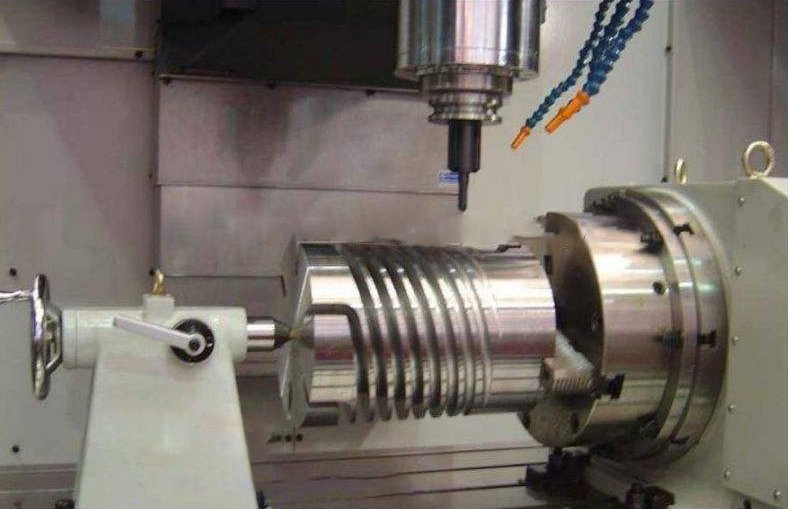

The future of machining will see even greater levels of automation, driven by advancements in technology. Key trends include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can optimize machining processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve decision-making.
Internet of Things (IoT): Connected machines and devices provide real-time data, enabling better monitoring and control of manufacturing processes.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots work alongside human operators, combining the precision of robots with the flexibility of human workers.
Conclusion
Automation is transforming the machining industry, offering numerous benefits in terms of productivity, quality, and cost efficiency. As technology continues to advance, the role of automation will become even more significant, driving the industry towards a more efficient and innovative future.